During the period of Muslim domination of the island, from the ninth to the eleventh century, Palermo was a rich and prosperous capital, with over 350 thousand inhabitants. 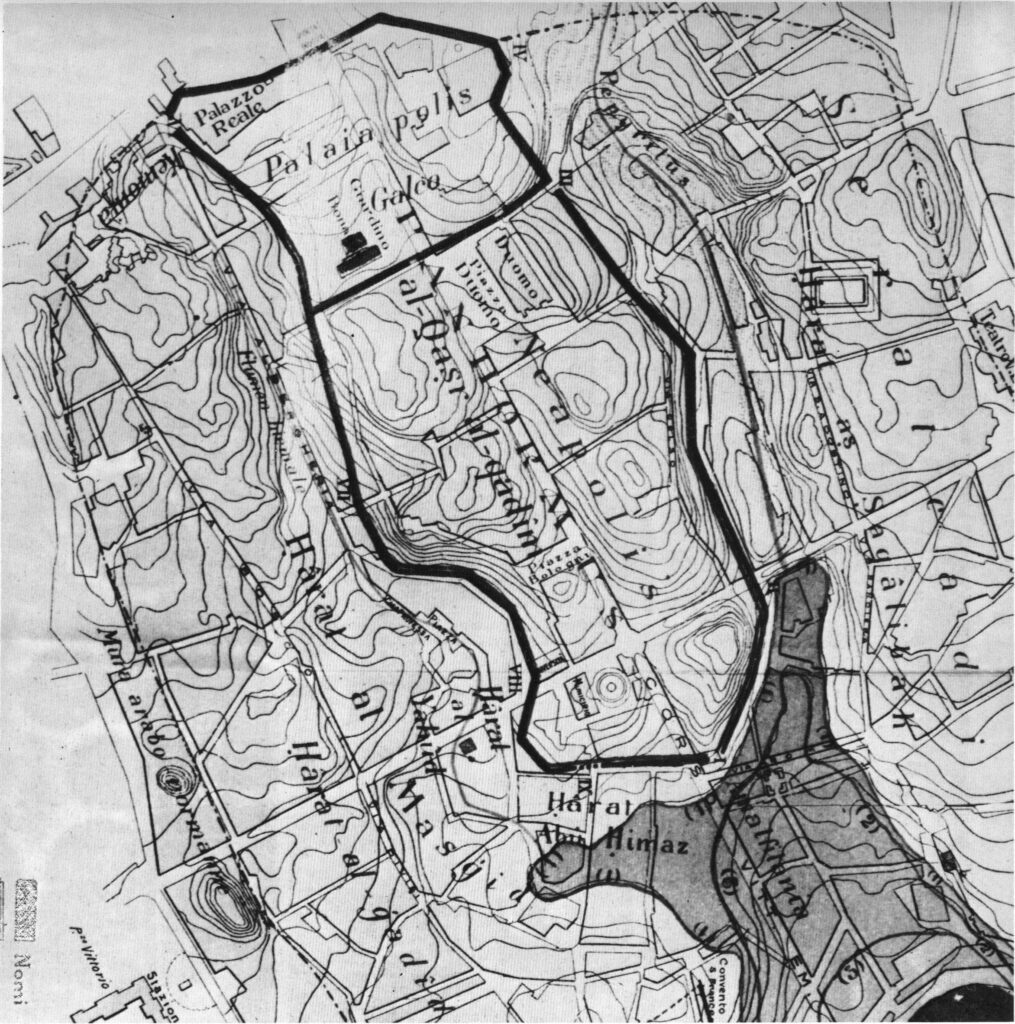 The city was the third most important throughout the Mediterranean, after the great Cordoba, belonging to the
emirate of Spain
The city was the third most important throughout the Mediterranean, after the great Cordoba, belonging to the
emirate of Spain
, and Constantinople, capital of the
Byzantine Empire
.
In his travel book, the Arab traveler
Ibn Hawqal
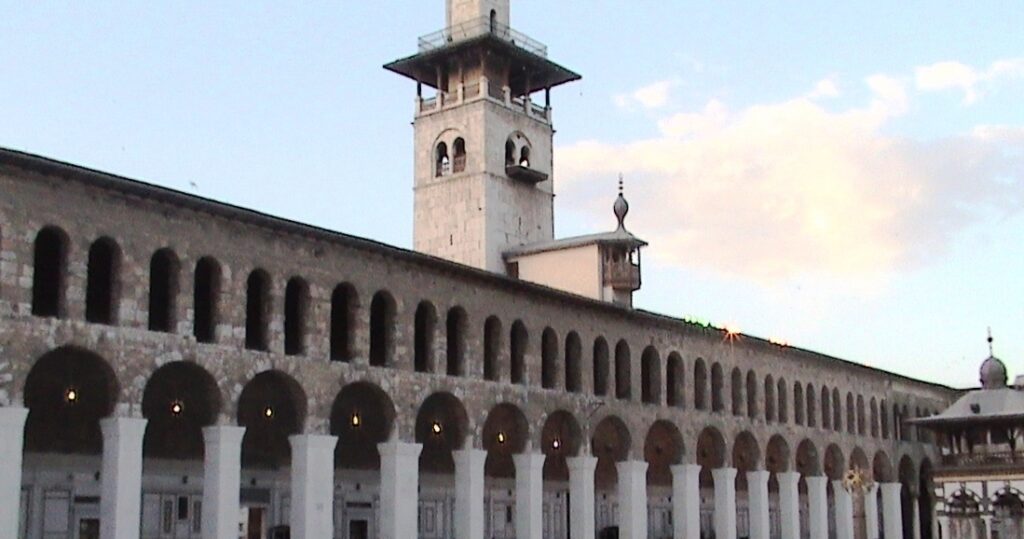
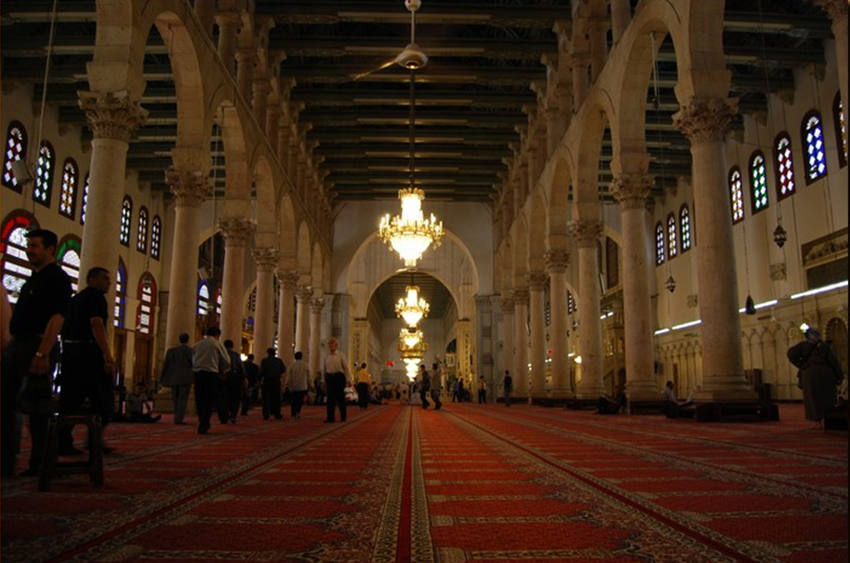
, who visited Sicily in 973, depicts the city as rich in lush gardens, large markets, and a centre of trade and commerce with the entire Mediterranean. He describes the multitude of mosques present in the city and, in particular, the great
Gami Mosque
(or ‘Friday Mosque’), which was probably built with reference to the
great Umayyad Mosque in Damascus
, taken as a model for all mosques in the Islamic world.


