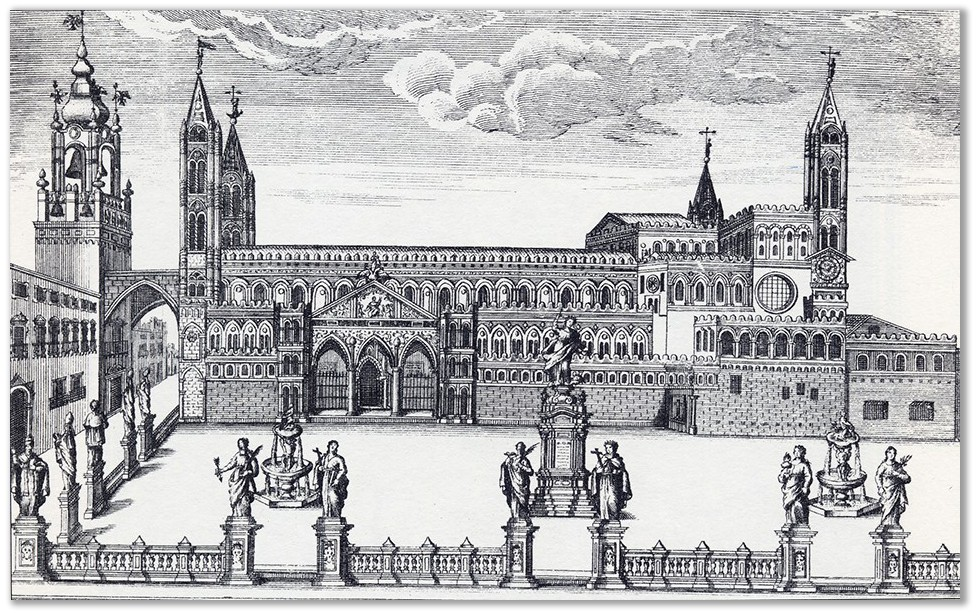
 The Palermo Cathedral had the distinction of being the largest church in terms of length, compared to other contemporary churches in Sicily, with reference to the
cathedral buildings in Cefalù, Catania and Messina
The Palermo Cathedral had the distinction of being the largest church in terms of length, compared to other contemporary churches in Sicily, with reference to the
cathedral buildings in Cefalù, Catania and Messina
. It is likely that this particular feature is due to the fact that the ‘Norman’ cathedral was built on the pre-existing great
Gami Mosque
in Palermo, while the other churches were built ‘ab fundamentis‘. Throughout the 12th century and part of the 13th century, the entrance to the Gualterian cathedral was located on the southern side, probably on the site of a pre-existing access room under the portico, also known as the
Loggia or Tocco
.
 The main or “canonical” west façade, left unfinished, began construction in the second half of the 13th century and was followed by the construction of the
large marble portal
The main or “canonical” west façade, left unfinished, began construction in the second half of the 13th century and was followed by the construction of the
large marble portal
, in around 1350, splayed with recessed lintels in the
late Romanesque
style.
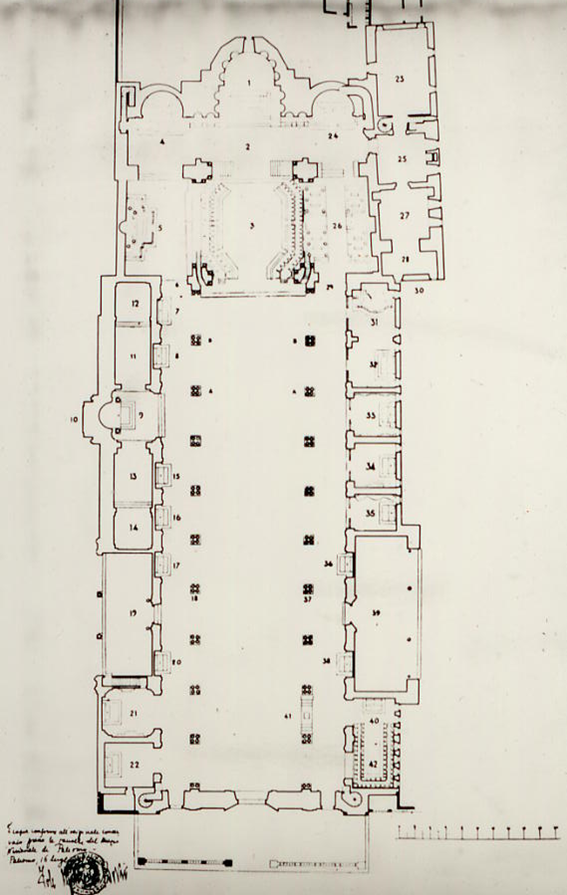
The hall was composed according to the canonical tripartition, divided by the arches that delimited the main aisle from the side aisles. It’s intended appearance was to appear very elegant and slender. The central part rose above the side walls with high walls on ten pointed archways on each side, supported by twenty-two groups of Egyptian granite columns, described by historians as
Theban columns
with
Tuscolan capitals
, using the
tetrastyle system
. This system was then followed during the Renaissance by
Giorgio di Faccio
, for the construction of the
San Giorgio dei Genovesi
Church in Palermo’s
Loggia dei Mercanti district
.
The central area was lit by large single-lancet windows, framed in the wall plane with an alternating score of voids and solids followed, on the external façade, by a series of blind single-lancet windows defined by arches with recessed lintels and framed by small marble and porphyry columns.