A volcano is the surface manifestation of magma, i.e. molten rock mixed with gas and vapour, at high temperatures. After its eruption on the surface, the molten material is called lava. When lava solidifies, it usually accumulates to form a volcanic structure.
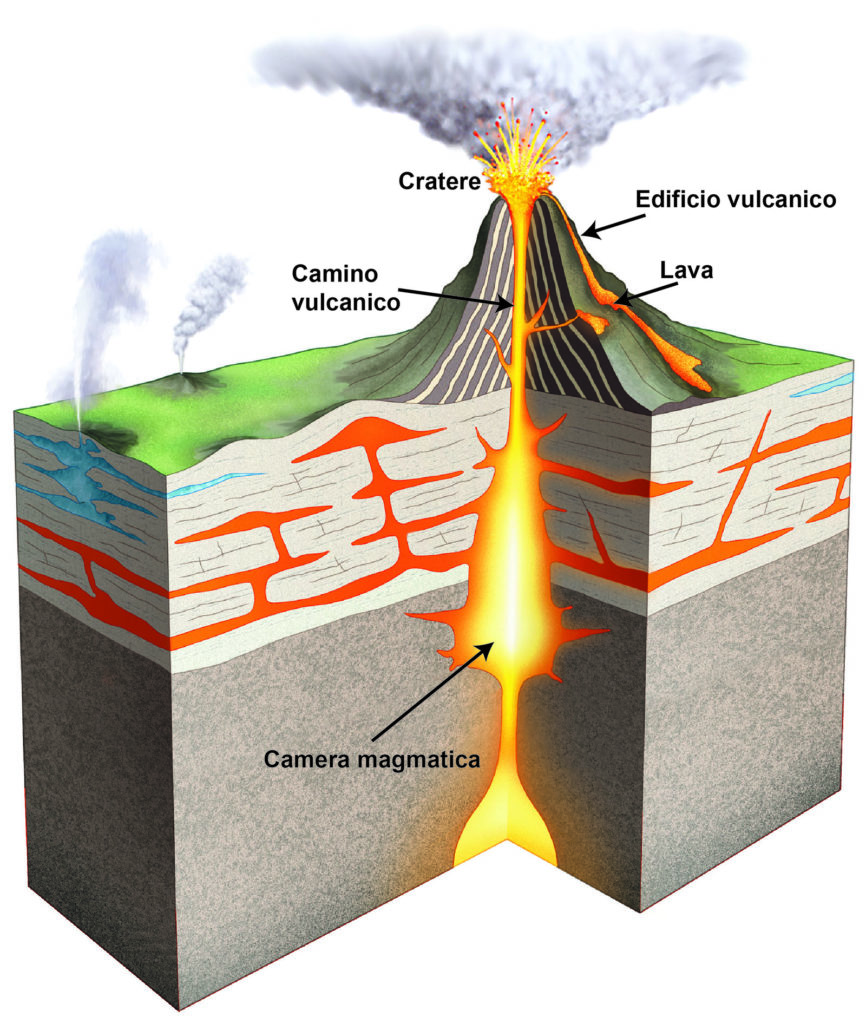
The most important parts of a volcano are:
The magma chamber: an area within the Earth where magma accumulates. Lava differs from volcano to volcano, especially in chemical composition, gas content and temperature.
These factors affect the viscosity of magma and therefore the speed at which the lava flows.
The solid fragments that are thrown out by a volcano are called
pyroclastic products
, and have very variable dimensions: volcanic ash; lapilli; volcanic bombs.