Due to the modifications and transformations carried out in the second half of the 12th century at the behest of Archbishop
Gualtiero
, the medieval layout of the Cathedral remained almost unchanged until the end of the 18th century, when the sacred building underwent a complex
renovation
, profoundly changing its original stylistic features, both inside and out.
During the period of Gualtiero, the ancient church, which had been used as a mosque at the time of the Muslim occupation, was radically restructured, and the double transept or
great Presbytery
system was created in the area of the sanctuary, composed of Titulo and Antititulo, according to the same construction scheme adopted in the contemporary
Monreale Cathedral
.
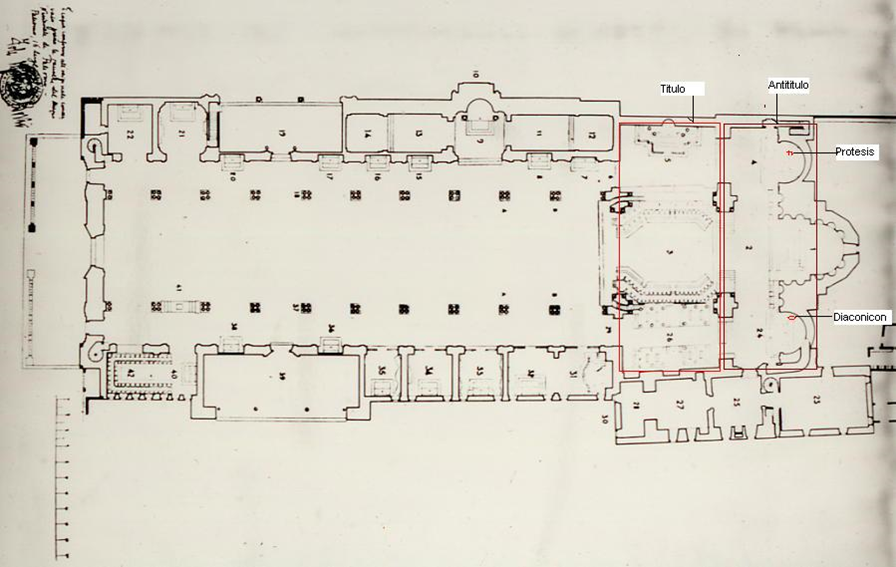 The renovation transformed the area at the end, towards the east, where the large central apse was created, as well as the two lateral ones. The right apse was used for
Diaconic
The renovation transformed the area at the end, towards the east, where the large central apse was created, as well as the two lateral ones. The right apse was used for
Diaconic
services, while the left one was used for
Prosthetic
services.
In the area in front of the three apses, the
Antititulo
was inserted. This is a transverse space with respect to the axiality of the church, functioning as an ambulatory in the area of the sanctuary. The Antititulo, as reported in the chronicles, was covered by a
muqarnas
ceiling, similar to that of the Palatine Chapel. This environment thus divided the area of the
apses
from the
Titulus
, a large square area including the choir, the
bishop's chair
and the royal seat, with the tombs of the Bishops and the cemetery of the Kings located on the left and right sides.
All these liturgical spaces formed the “great Presbytery”, separated from the naves, reserved for the faithful, by an
iconostasis
, according to the
Greek rite
, officiated in churches at that time, together with the Latin one. The Titulo area was lit by four large single-lancet windows, on the south and north fronts, with the outer frames decorated with Islamic-style “cushion rings”.
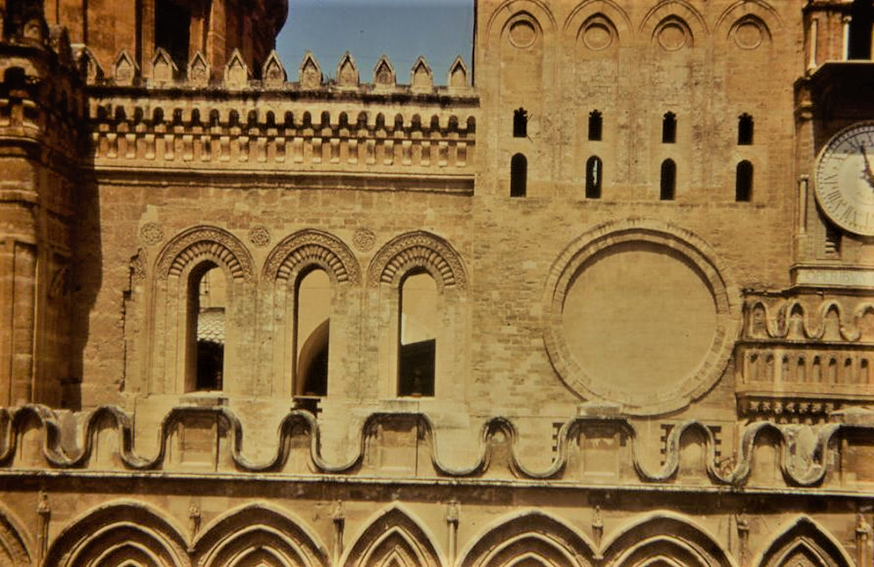 After the great transformation in the 18th century, only three remained on the southern side.
After the great transformation in the 18th century, only three remained on the southern side.
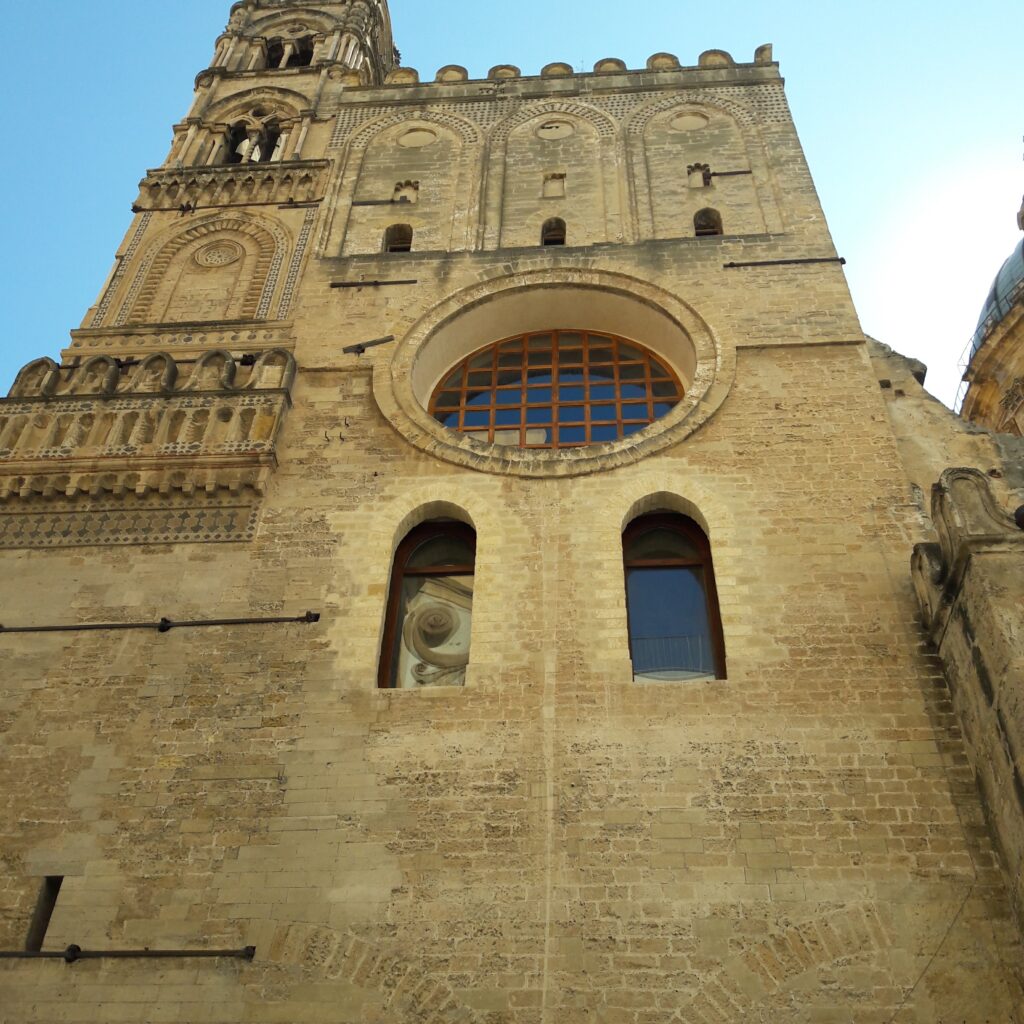
The Antititulo received light from a triad of lights, consisting of a large oculus and two single-lancet windows, open in the short walls to the north and south.
The Oculus was closed during restoration work carried out at the end of the 18th century and the two single-lancet windows were partly concealed beforehand.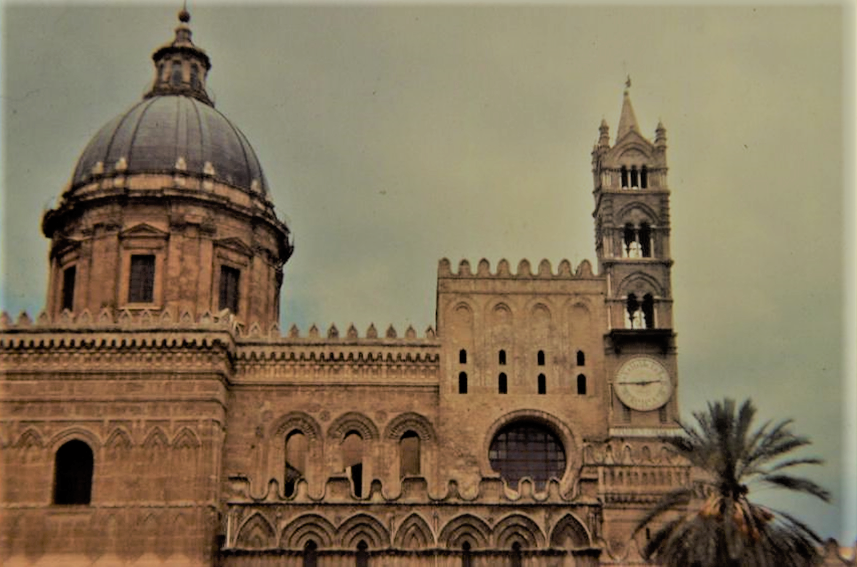
Recent restorations have restored the original openings, on the southern and northern fronts, although they have now lost their original function due to the changes made to the interior of the building.