The southern front of the Cathedral is the most articulated part of the sacred building. Its imposing bulk can be appreciated from the front floor, which includes the entire volume.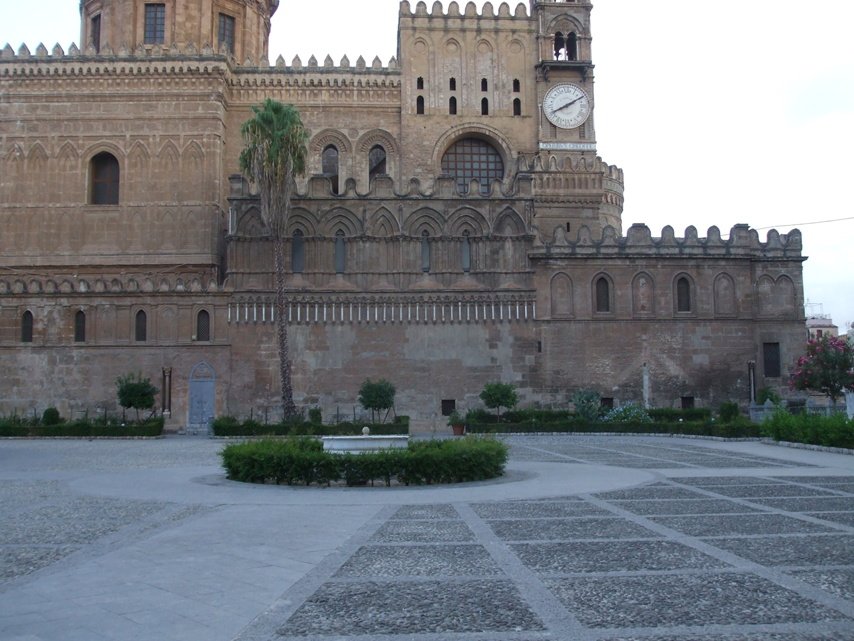 The church underwent various modifications over the centuries and this part lent itself well to subsequent extensions, thanks to the open space in front of it, which allowed the addition of external volumes.
The church underwent various modifications over the centuries and this part lent itself well to subsequent extensions, thanks to the open space in front of it, which allowed the addition of external volumes.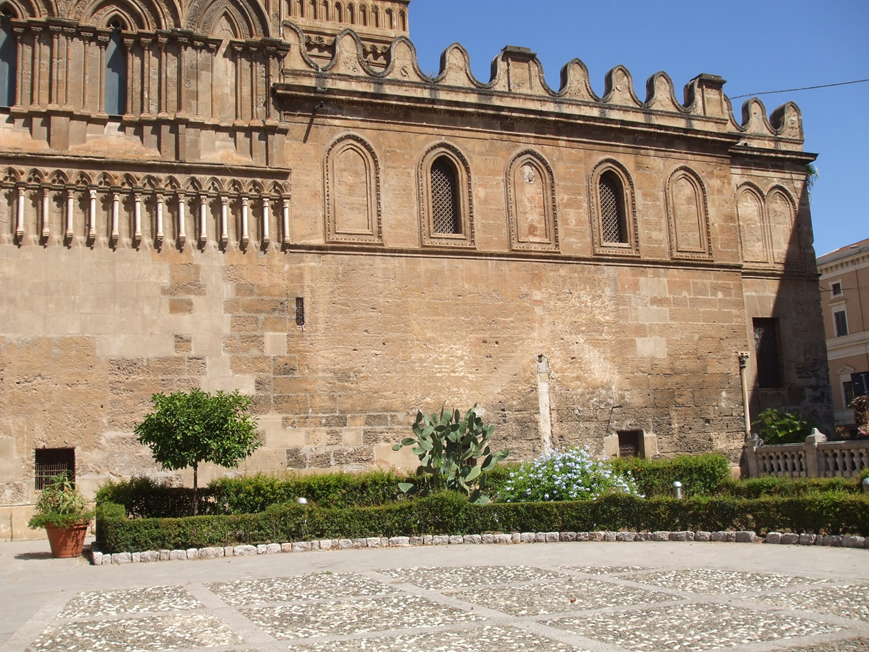
During the
transformation works
carried out at the end of the 18th century, a number of structures were built on this front, added to the right side aisle, enlarging and modifying the chapels that had previously existed with the creation of the Beneficiali Sacristy.
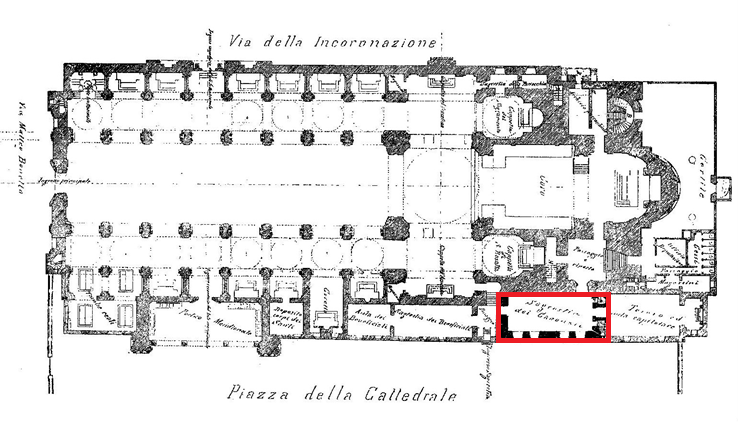 These changes resulted in a new alignment of the outer walls, incorporating the western side of the former Sacristy of the Canons. As early as the 16th century, it was concealed on its eastern front, where a building was constructed to house the
Cathedral's treasury
These changes resulted in a new alignment of the outer walls, incorporating the western side of the former Sacristy of the Canons. As early as the 16th century, it was concealed on its eastern front, where a building was constructed to house the
Cathedral's treasury
. The Sacristy of the Canons features its southern elevation, the only one visible today, composed of two distinct parts. The basement area is attributable to a medieval architectural building, characterised by a cornice, which was the terminal
cymatium
of the original building, decorated with blind
trefoil arches
, interspersed with
antefixes
with anthropomorphic representations and hanging nail columns. The upper part comes from a 15th-century
Gothic elevation
, the facing of which is enlivened by a series of single-lancet windows with an alternating open-closed rhythm, with recessed pointed arches and rich floral decoration carved into the wall face. Historical reconstruction and architectural analysis can lead to this building being identified, in its basement part, with the ancient Chapel of St. Mary Magdalene.